# MongoDB and ExpressJS
# Getting started
# Install MongoDB
Download and install MongoDB (opens new window)
# Install MongoDB Compass
Download and install MongoDB Compass (opens new window)
# Connect Express app to MongoDB
# Install Mongoose
Run the following command in backend/ to install Mongoose (opens new window)
npm install mongoose
Run the following command in backend/ to install dotenv (opens new window)
npm install dotenv
Create .env in the /backend/ directory and add the MONGO_URI environment variable and set it to your MongoDB connection string.
PORT=5000
MONGO_URI=mongodb://localhost:27017/blog_app
Import dotenv into app entry point file src/index.js
const express = require("express");
require("dotenv").config();
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 8000;
app.use(express.json());
app.use("/api/blogs", require("./routes/blogs"));
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`IX blogging app listening on port ${port}`);
});
*Note: The update to the port. The port os now coming from the environment variables.
# Connect to MongoDB
# Implement Mongoose
In backend/src/ create a database directory and add a file called db.js
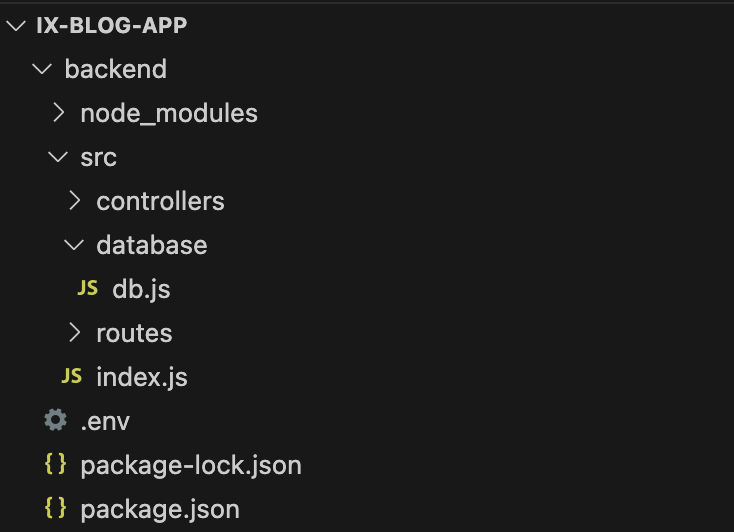
# Connect to MongoDB
Add the following boilerplate db code to src/database/db.js:
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const connectDB = async () => {
try {
const conn = await mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
});
console.log(`MongoDB Connected: ${conn.connection.host}`);
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Error: ${error.message}`);
process.exit(1);
}
};
module.exports = connectDB;
Import and execute connectDB in project entry file, src/index.js:
const express = require("express");
const connectDB = require("./database/db");
require("dotenv").config();
connectDB();
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 8000;
app.use(express.json());
app.use("/api/blogs", require("./routes/blogs"));
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`IX blogging app listening on port ${port}`);
});
# Models
Models are the Model part of the MVC software architectural pattern.
Represents the UI of the application. It displays data (the model) to the user and sends user commands (events) to the controller. The view is responsible for rendering the data provided by the model in a format suitable for interaction, typically through a user interface.
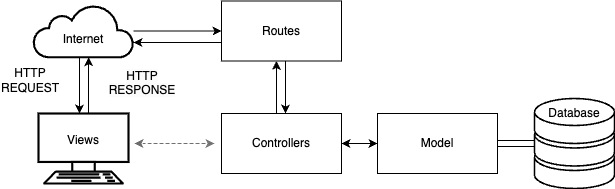
# Create Blog Model
In backend/src/ create a models directory and add a file called blogModel.js
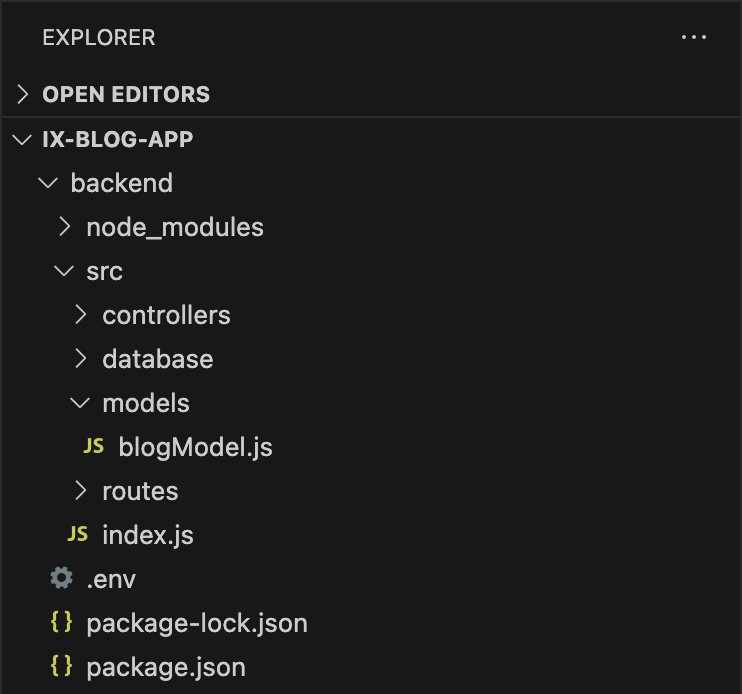
# Define Blog Model
Add the following code to define the blog model in src/models/blogModel.js:
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
const blogSchema = new mongoose.Schema(
{
authorId: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
categoryId: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
title: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
description: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
image: {
type: String,
required: true,
},
content: {
type: Array,
required: true,
},
},
{ timeStamp: true }
);
module.exports = mongoose.model("Blog", blogSchema);
# CRUD
# Blog CRUD using the blog model
Import Blog model into src/controllers/blogs.js
const Blog = require("../models/blogModel");
Update the createBlog function in the blogs controller to use the Blog model.
- createBlog function is converted to async since
await blog.save();is asynchronous. - Try catch error handling.
- req.body cast to Blog.
const createBlog = async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = new Blog({
authorId: req.body.authorId,
categoryId: req.body.categoryId,
readTime: req.body.readTime,
title: req.body.title,
description: req.body.description,
image: req.body.image,
content: req.body.content,
});
const newBlog = await blog.save();
res.status(201).json({ message: "New blog created!", data: newBlog });
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: error.message, data: [] });
}
};
Update the getBlogs and getBlog functions in the blogs controller to use the Blog model.
const getBlogs = async (req, res) => {
try {
const blogs = await Blog.find();
res.status(200).json({ message: "Return all blogs!", data: blogs });
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: error.message, data: [] });
}
};
const getBlog = async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.findById(req.params.id);
if (blog) {
res.status(200).json({ message: "Return blog by ID!", data: blog });
} else {
res.status(404).json({ message: "Blog not found!", data: [] });
}
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: error.message, data: [] });
}
};
Update the updateBlog function in the blogs controller to use the Blog model.
const updateBlog = async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.findById(req.params.id);
if (blog) {
blog.authorId = req.body.authorId || blog.authorId;
blog.categoryId = req.body.categoryId || blog.categoryId;
blog.title = req.body.title || blog.title;
blog.description = req.body.description || blog.description;
blog.image = req.body.image || blog.image;
blog.content = req.body.content || blog.content;
const updatedBlog = await blog.save();
res.status(200).json({ message: "Blog updated!", data: updatedBlog });
} else {
res.status(404).json({ message: "Blog not found!", data: [] });
}
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ message: error.message, data: [] });
}
};
Update the deleteBlog function in the blogs controller to use the Blog model.
const deleteBlog = async (req, res) => {
try {
const blog = await Blog.findByIdAndDelete(req.params.id);
if (blog) {
return res.status(200).json({ message: "Blog deleted!" });
} else {
return res.status(404).json({ message: "Blog not found!" });
}
} catch (error) {
return res.status(500).json({ message: error.message });
}
};